If you’ve ever Googled "CFD meaning", chances are you’re curious about online trading. Maybe you’ve seen ads promising flexible trading opportunities, or perhaps someone mentioned CFDs in a financial discussion. But what exactly is CFD and how does CFD trading work?
This guide will break down CFD meaning, how CFDs function, the benefits and risks involved, and how you can start trading with confidence. No jargon, no complicated financial talk—just a clear roadmap for beginners.
Quick Summary:
-CFD stands for “Contract for Difference” – it lets you speculate on price movements of assets without owning them.
-You can trade rising and falling markets by opening long (buy) or short (sell) positions.
-Leverage amplifies both potential profits and losses, so risk management is crucial.
-CFDs cover a wide range of markets: stocks, indices, forex, commodities, and even cryptocurrencies.
-Most beginner accounts lose money when trading CFDs – practice on a demo account before going live.
-Key risks include market volatility, overtrading, and broker insolvency – always trade with a regulated provider.
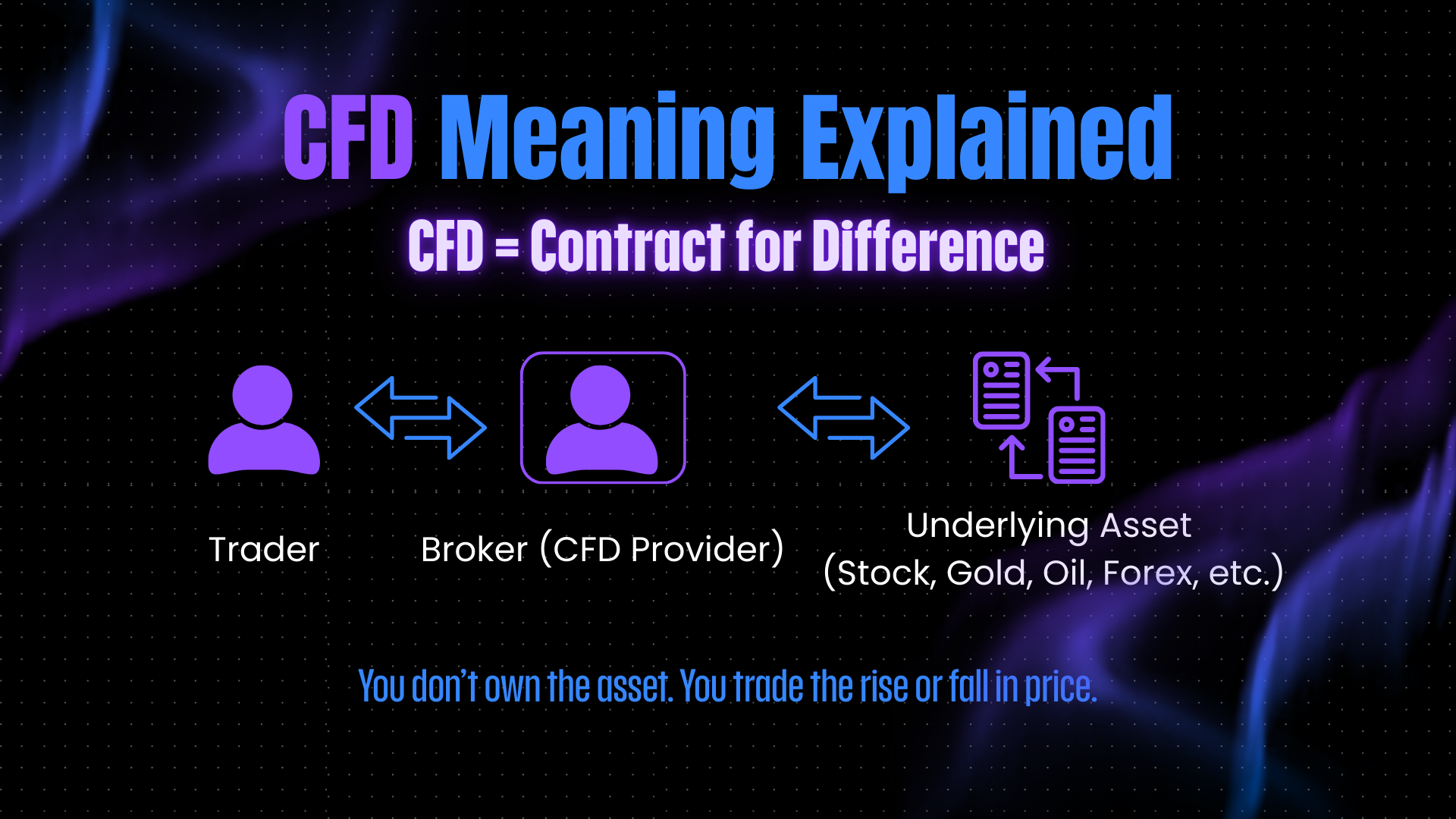
What Is a CFD? (CFD Meaning Explained)
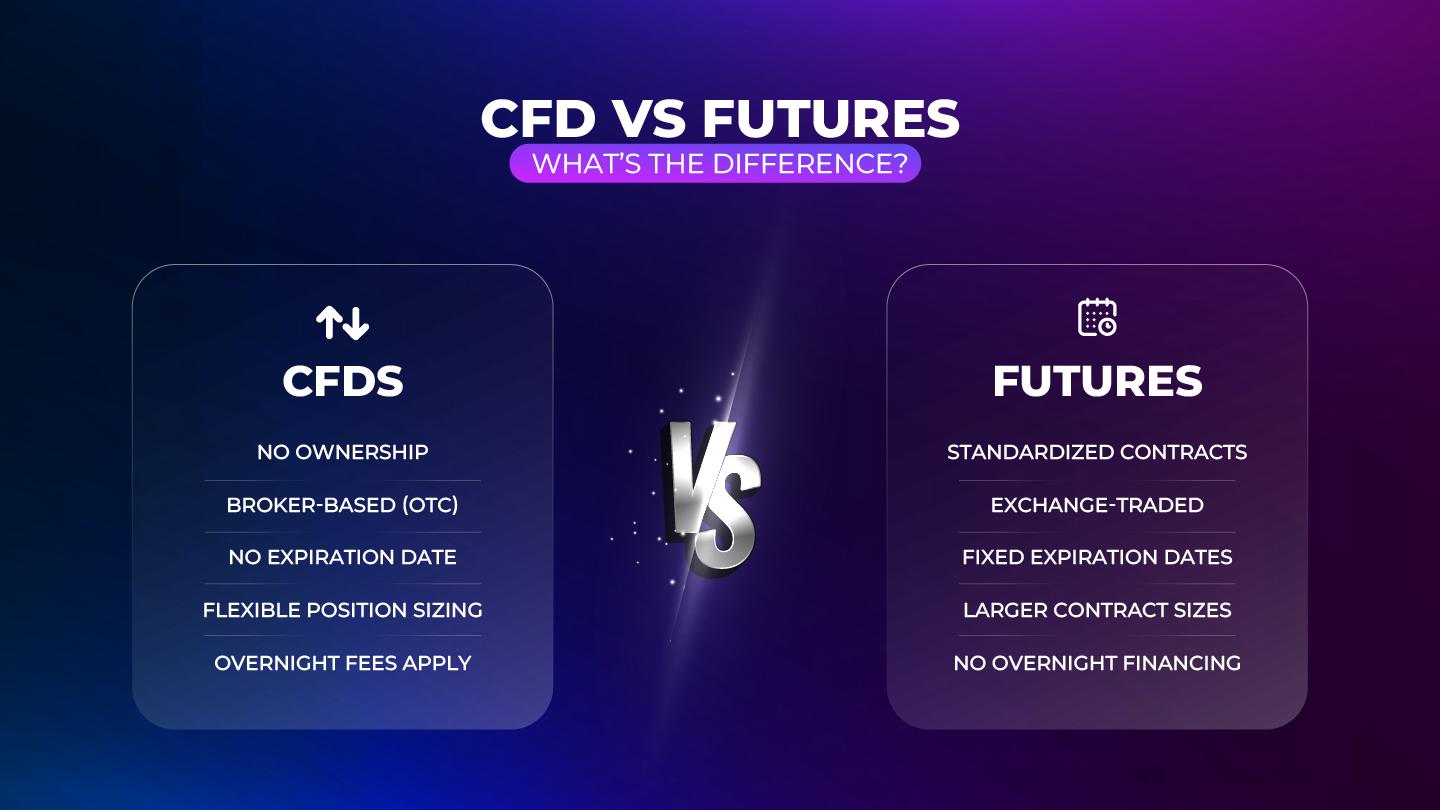
CFD stands for Contract for Difference. It’s a type of financial derivative that allows you to speculate on the price movements of various assets without actually owning the underlying asset.
In simpler terms, when you trade a CFD, you’re entering a contract with a broker. You’re betting on whether the price of an asset—like a stock, index, commodity, or currency—will go up or down. If your prediction is correct, you profit from the price difference. If you’re wrong, you lose money.
Example of How CFDs Works:
Let’s say you believe the price of the Gold financial instrument is going to rise.
-
Current Gold price of the underlying asset: $1,900 per ounce.
-
You open a buy (long) CFD position at this price.
-
Later, Gold’s price rises to $1,950 per ounce.
-
You close your position, and you profit from the $50 price difference (multiplied by the contract size).
If the price had fallen instead, you would have lost the difference.
Key Features of CFD Trading
Now that you understand the basic CFD meaning, let’s dive deeper into how CFDs work and why traders use them.
1. Trading Price Movements, Not Assets
With CFDs, you don’t buy or sell the actual asset. You’re simply speculating on whether the price will rise or fall. This makes CFDs more flexible than traditional investing.
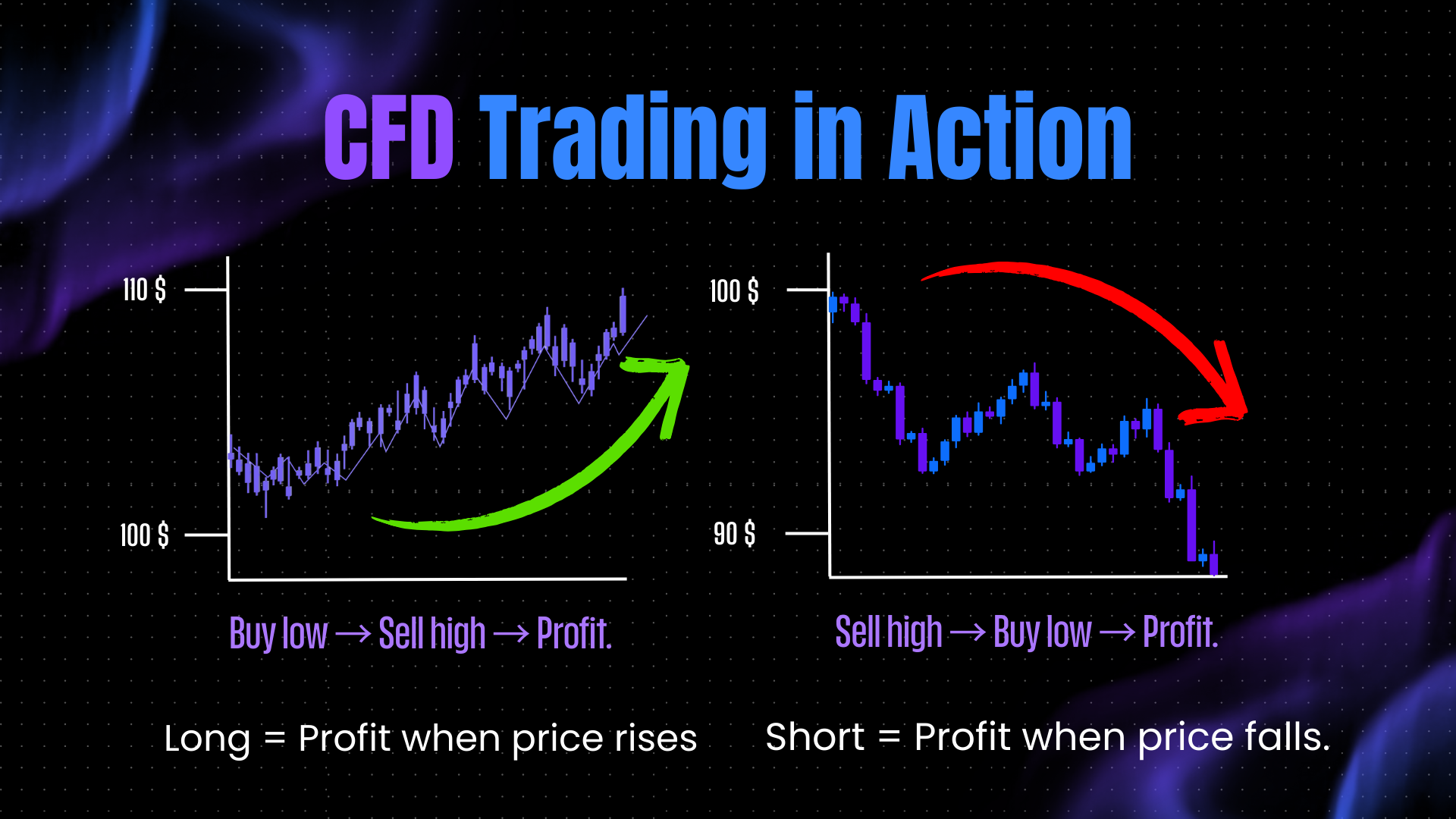
2. Long and Short Positions
-
Going Long: You believe the price will go up, so you open a buy position.
-
Going Short: You believe the price will go down, so you open a sell position.
This two-way trading is a major advantage for people who want to profit in both rising and falling markets.
3. Leverage
CFD trading usually involves leverage, meaning you only need to deposit a fraction of the total trade value (margin requirement). This can amplify your profits—but it also magnifies your losses.
4. Wide Range of Markets
CFDs cover a broad spectrum of financial markets, including:
-
Stocks and shares
-
Indices (e.g., S&P 500, FTSE 100)
-
Forex (currency pairs)
-
Commodities (e.g., gold, oil)
-
Cryptocurrencies (some brokers offer crypto CFDs)

Advantages of CFD Trading
Trading CFDs has several benefits, especially for beginners looking to enter the financial markets without needing large amounts of capital.
1. Access to Global Markets
CFDs are traded on a wide variety of global markets from a single cfd provider trading platform. Whether you’re interested in U.S. tech stocks or commodities like oil, you can find CFDs for almost any market.
2. Use of Leverage
Leverage means you can control a larger position with a smaller deposit. For example, if a broker offers 10:1 leverage, you only need to deposit $100 to control a $1,000 trade.
Warning: Leverage is a double-edged sword. It can increase potential profits but also lead to significant losses.
3. Ability to Short-Sell Easily
With traditional investing, making money when prices fall is difficult. CFDs make it simple to short-sell, allowing you to profit from declining markets.
4. No Stamp Duty (in Some Countries)
In places like the UK, CFD trading avoids stamp duty because you’re not actually buying shares. However, tax laws vary, so check your local regulations.
5. Flexible Trading Hours
Many CFD markets are open 24/5, and some (like cryptocurrencies) are available 24/7. This allows traders to react to market news at almost any time.
Risks of CFD Trading
While CFDs offer opportunities, they also come with risks. Here’s what beginners need to know:
1. Leverage Risk
Leverage can work against you just as easily as it can work for you. A small price movement in the wrong direction can wipe out your trading account if you’re over-leveraged.
2. Market Volatility
Markets can be unpredictable. Prices can move quickly due to economic news, company earnings, political events, or even rumors.
3. Overtrading
Because CFD trading is accessible and fast, some beginners fall into the trap of overtrading—making too many trades without a clear strategy. This can lead to significant losses.
4. Counterparty Risk
When you trade CFDs, you’re entering a contract with a broker, not an exchange. If the broker goes out of business, your accounts lose money, and you might not get your money back. Make sure you use a regulated and reputable broker.
5. Fees and Costs
CFD trading often involves costs like:
-
Spreads: The difference between the buy and sell price.
-
Overnight Financing Fees: If you hold a position overnight, you might pay a fee.
-
Commission (in some cases): Some brokers charge a commission on trades, especially for shares.
How to Start Trading CFDs – A Beginner’s Checklist
Ready to give CFD trading a try? Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started safely and smartly.
1. Learn the Basics
Before placing your first trade, take time to understand:
-
How leverage works
-
How to manage risk
-
How to read charts and market trends
2. Choose a Trusted CFD Broker
Look for a broker that offer cfds and is:
-
Regulated by a financial authority
-
Offers competitive spreads and transparent fees
-
Provides a user-friendly platform
-
Has good educational resources for beginners
3. Open a Demo Account
Practice with virtual money first. A demo account lets you learn the ropes without risking real capital. It’s important to remember that accounts lose money when trading
4. Start Small
When you move to live trading, start with small trades. This allows you to manage risk while you gain experience.
5. Use Risk Management Tools
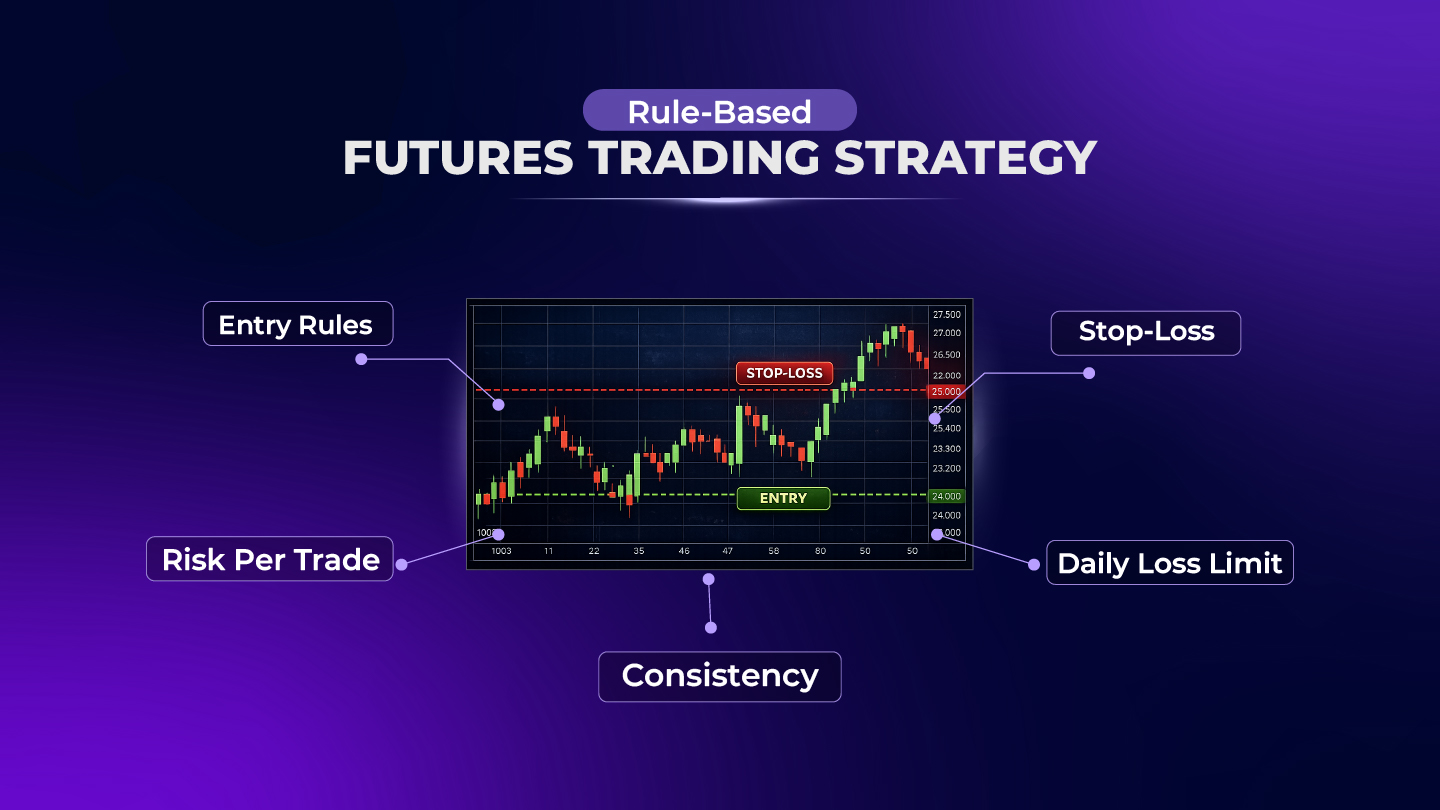
Successful CFD traders use:
-
Stop Loss Orders: Automatically close a trade to limit losses since most traders lose money when trading cfds.
-
Take Profit Orders: Lock in profits when the market reaches a target price.
-
Trailing Stops: Follow the market direction to maximize gains while protecting profits.
6. Stay Informed
Financial markets are influenced by news, events, and economic data. Stay updated by:
-
Reading financial news
-
Following market analysis
-
Watching economic calendars
7. Keep Emotions in Check
Trading can be emotional. Fear and greed often lead to bad decisions and increase the risk of losing your capital. Stick to your plan and avoid impulsive trades.
Common Beginner Mistakes with CFD Trading (And How to Avoid Them)
Understanding CFD meaning is only part of becoming a successful trader. The other part is knowing what not to do. Many beginners fall into the same traps when they first start trading CFDs. Here’s a look at the most common mistakes—and how you can avoid them.
1. Overusing Leverage
Leverage is one of the biggest attractions in CFD trading. It allows you to control and buy a cfd with a smaller amount of capital. But leverage is a double-edged sword. While it can magnify your profits, it can also amplify your losses just as quickly.
The Mistake:
Beginners often use the maximum leverage offered by their broker, thinking it’s the fastest way to make money.
The Fix:
Start with low leverage until you understand how CFD trading works. Always know the risk before you trade as it will give you better control of your account’s profit and loss levels.
2. Ignoring Stop Losses
A stop loss is a tool that automatically closes your trade at a pre-set price to limit losses. Ignoring stop losses is like driving without brakes.
The Mistake:
New traders sometimes avoid setting stop losses because they think the market will “come back” in their favor. This often leads to mounting losses.
The Fix:
Always use cfds stop loss when opening a CFD position. Decide in advance how much you’re willing to lose and stick to it. It’s a basic but essential part of risk management.
3. Trading Without a Plan
Trading CFDs without a strategy is like gambling at a casino. You might win by luck a few times, but over the long term, you’re likely to lose.
The Mistake:
Many beginners jump into trades based on gut feelings or random tips from social media.
The Fix:
Create a trading plan before you start. This should include:
-
Your strategy (trend following, swing trading, etc.)
-
Entry and exit points
-
Risk management rules
-
A review process to learn from each trade
4. Chasing Losses (Revenge Trading)
Sometimes a trade goes wrong, and beginners try to recover their losses by immediately entering another trade—often without thinking it through.
The Mistake:
Trying to “win back” money by trading emotionally usually leads to even bigger losses.
The Fix:
Take a break after a losing trade. Clear your mind, review what happened, and stick to your plan. Successful trading requires discipline, not desperation.
5. Overtrading
CFD trading platforms are accessible 24/5 (and in some cases, 24/7). This convenience can tempt beginners into placing too many trades too quickly.
The Mistake:
Opening multiple positions at once or trading every small market movement without proper analysis.
The Fix:
Focus on quality over quantity. Wait for the right setups that match your strategy. Remember, trading is not about being busy—it’s about being effective.
6. Ignoring Trading Costs
Even though many brokers advertise “commission-free” CFD trading, that doesn’t mean it’s free. Costs like spreads, overnight financing fees, and swap charges can eat into your profits.
The Mistake:
Beginners often forget to factor in these costs, which can turn a winning trade into a losing one.
The Fix:
Understand all the fees before you start trading. Choose brokers with tight spreads and transparent pricing. If you plan to hold trades overnight, be aware of overnight charges.
7. Failing to Keep Emotions in Check
CFD trading can be exciting, but emotions like fear, greed, and frustration often lead to poor decisions.
The Mistake:
Panic-selling when the market moves against you or holding onto losing trades out of stubbornness.
The Fix:
Stick to your trading plan. Use stop losses and take profit targets to automate decisions and reduce emotional trading.
CFD Trading Strategies for Beginners
Understanding CFD meaning is only the first step. To trade CFDs successfully, you need a strategy. Trading without a plan is like driving blindfolded—you’re more likely to crash than arrive at your destination.
Here are some beginner-friendly CFD trading strategies to consider:
1. Trend Following
This strategy is based on the idea that “the trend is your friend.” You aim to enter trades in the direction of the current market trend.
How to Use It:
-
Identify whether the market is in an uptrend (prices making higher highs and higher lows) or a downtrend (prices making lower highs and lower lows).
-
Use technical indicators like moving averages or trendlines to confirm the trend.
-
Open a buy (long) position in an uptrend or a sell (short) position in a downtrend.
Pros:
-
Easy for beginners to understand.
-
Works well in strong trending markets.
Cons:
-
Not effective in sideways or choppy markets.
-
Requires patience—trends don’t last forever.
2. Breakout Trading
Breakout trading involves entering a position when the price breaks through a key level of support or resistance.
How to Use It:
-
Watch for price consolidation (when the market moves in a tight range).
-
Place a trade when the price breaks out of this range, signalling the start of a new trend.
Tools to Help:
-
Support and resistance levels
-
Volume indicators (breakouts with strong volume are usually more reliable)
Pros:
-
Helps catch big moves early.
-
Can be combined with trend following.
Cons:
-
False breakouts (called “fakeouts”) are common.
-
Requires quick decision-making.
3. Swing Trading
Swing trading is about capturing short- to medium-term price moves over several days or weeks.
How to Use It:
-
Look for markets that are swinging between highs and lows.
-
Enter trades at the start of a new price swing, then exit when the move runs out of momentum.
Pros:
-
Less time-intensive than day trading.
-
Good for people with day jobs who still want to trade.
Cons:
-
Markets can reverse unexpectedly.
-
Overnight risks (like unexpected news) can affect open positions.
4. Scalping
Scalping involves making many small trades throughout the day, aiming to profit from minor price changes.
How to Use It:
-
Use short timeframes (like 1-minute or 5-minute charts).
-
Focus on assets with high liquidity and tight spreads.
Pros:
-
Can generate quick returns.
-
Low exposure to market events.
Cons:
-
Requires fast decision-making and lots of screen time.
-
Small mistakes can add up to big losses.
Important Note on Strategies
No strategy guarantees profits. The goal is to find a trading style that fits your personality, time commitment, and risk tolerance. Always test strategies on a demo account before risking real money.
Risk Management Is Part of Every Strategy
No matter which CFD strategy you choose, risk management is critical. This includes:
-
Setting stop losses and take profit levels
-
Only risking a small percentage of your trading capital per trade
-
Keeping emotions out of your decision-making process
Common Questions About CFD Trading
Is CFD Trading Legal?
In most countries, yes—but some places like the U.S. restrict CFD trading for retail traders. Always check local regulations.
Do I Own the Assets When Trading CFDs?
No. You never own the actual asset. You’re trading a contract that mirrors the asset’s price movements.
How Much Money Do I Need to Start?
Many brokers allow you to start with as little as $100. However, trading with too small a balance can increase risk due to leverage.
Can I Trade CFDs Full-Time?
Some experienced traders do. But for beginners, it’s usually better to start part-time while learning the ropes.
Final Thoughts: Should You Trade CFDs?
CFD trading offers a flexible way to access financial markets without buying the actual assets. It’s popular because of its versatility—you can trade rising and falling markets, use leverage, and access a broad range of markets from one platform.
But CFDs are not risk-free. The same tools that make them attractive—like leverage and short-selling—can also lead to quick losses if you’re not careful.
If you’re a beginner searching for "CFD meaning", the most important thing is to educate yourself, start small, and use risk management strategies. Practice first, and when you’re ready to go live, trade responsibly.