overlooked, or written off as red flags. But if you know what to look for, these corporate moves can offer smart traders a chance to profit. So, how do you profit from a reverse stock split?
In this guide, we break it all down—what reverse stock splits are, why they happen, how they impact a stock's price and investor psychology, and most importantly, how to trade around them.
Let’s get into it.
Quick Summary
Wondering how to profit from a reverse stock split? While reverse splits don’t increase a company’s value, they often create short-term trading opportunities due to reduced float, increased volatility, and shifts in trader sentiment.
Smart traders use strategies like:
-
Trading the post-split bounce
-
Shorting the hype after the spike
-
Exploiting float squeezes in low-float stocks
-
Using options (when available)
-
Swinging the longer-term fade
The key is to trade the reaction—not the event itself. Focus on volume, float, and setup quality, and avoid low-liquidity traps or dilution-heavy companies. With the right timing and discipline, reverse stock splits can become a high-reward corner of your trading playbook.
What Is a Reverse Stock Split?
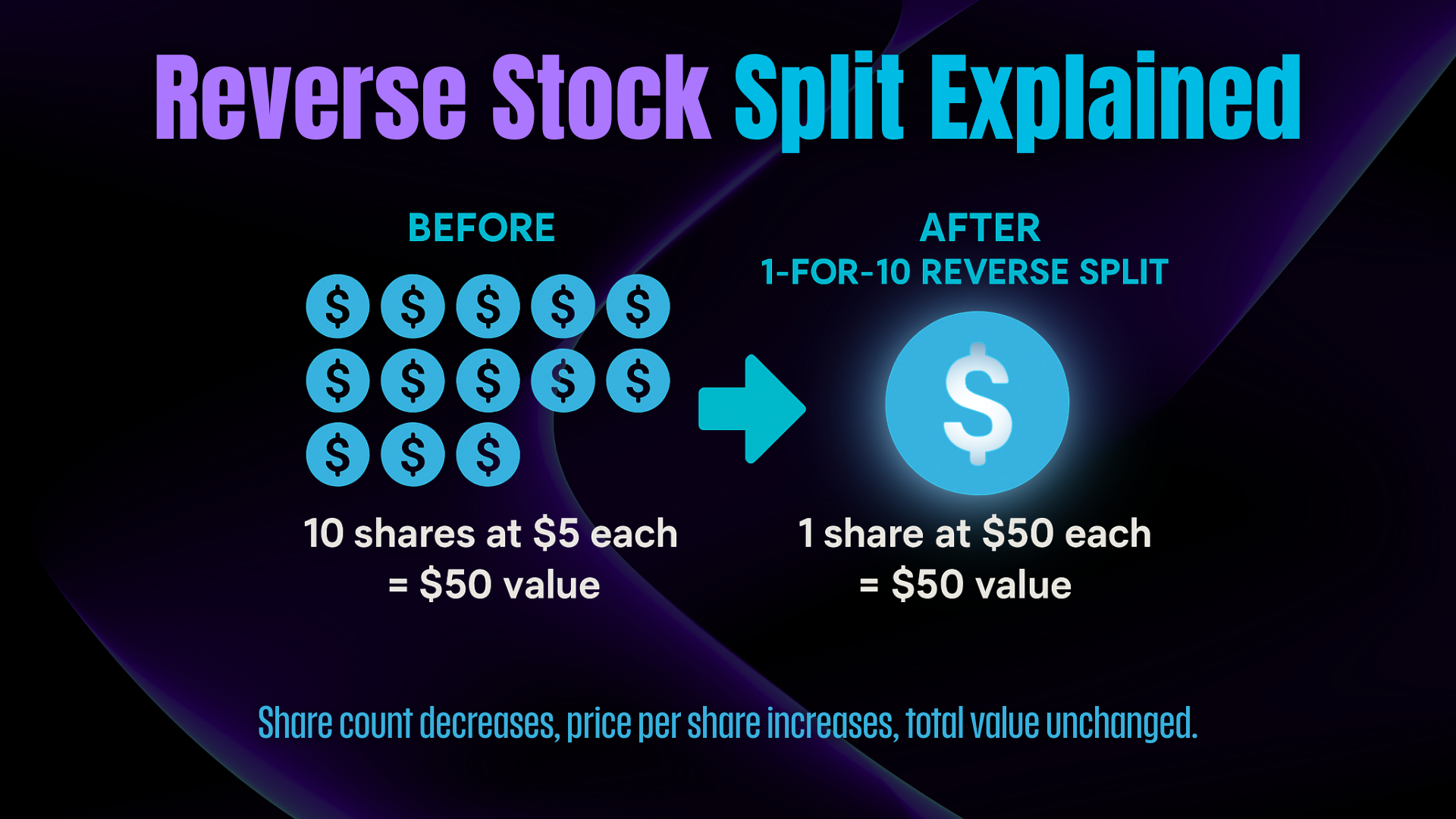
A reverse stock split is a corporate action in which a company decides to reduce the number of its outstanding shares while increasing the share price proportionally. The company’s market capitalization remains the same—at least on paper.
Example:
If a company does a 1-for-8 reverse stock split, that means every 8 shares you own are consolidated into 1 share, and the price per share increases by 8x.
-
Before: 800 shares at $0.50 = $400
-
After: 80 shares at $5.00 = $400
The total value of your position doesn’t change immediately, but the optics and dynamics of the stock change significantly.
Why Do Companies Do Reverse Stock Splits?

Companies typically use reverse stock splits to:
-
Avoid delisting from stock exchanges (many exchanges have minimum price requirements, like $1 on the NASDAQ).
-
Improve the stock’s appearance to institutional investors or retail traders.
-
Reduce volatility and speculative activity by consolidating the number of shares and raising the price.
In many cases, the underlying company is struggling, which is why reverse splits are often seen as a last-ditch effort. But that’s where opportunity hides.
Do Reverse Stock Splits Increase Value?
No. A reverse stock split doesn’t increase a company’s actual value. It’s purely cosmetic. However, it can influence perception, attract new buyers, and change the way traders interact with the stock.
That’s where savvy traders come in.
How to Profit from a Reverse Stock Split
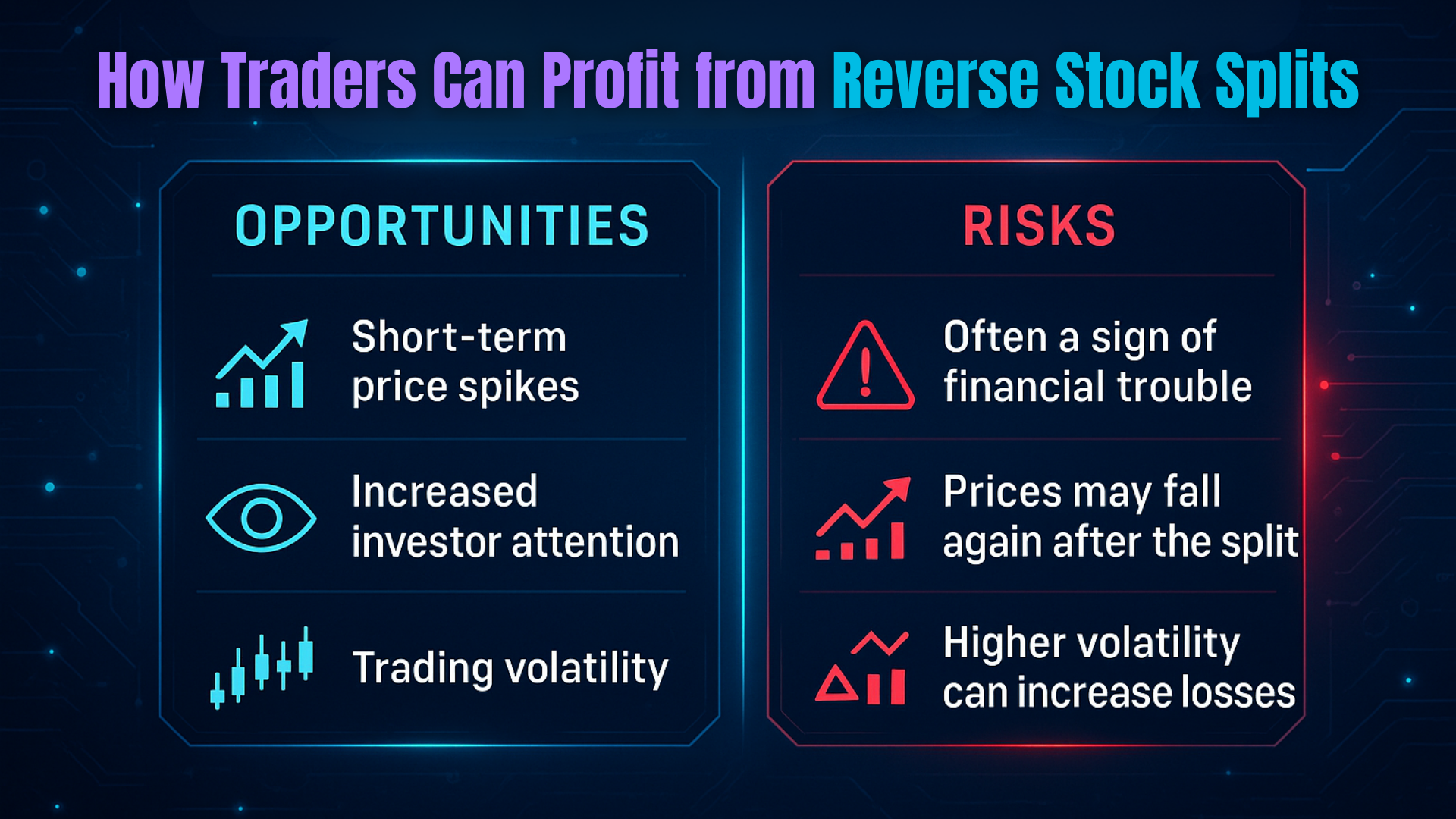
Here’s the real reason you’re here: how to profit from a reverse stock split. Below are the key strategies successful traders use to capitalize on these corporate actions.
1. The Post-Split Bounce Strategy
How It Works:
Some reverse split stocks experience a short-term bounce right after the split due to reduced float and a higher per-share price.
Why It Works:
-
The reduced number of shares outstanding can lead to increased volatility.
-
Higher price points can attract new types of buyers (e.g., institutions or options traders).
-
Traders who shorted the stock pre-split may cover positions, adding to buying pressure.
How to Trade It:
-
Monitor stocks with recent or upcoming reverse splits.
-
Look for strong pre-market volume and gap-up behavior.
-
Enter after confirmation of a breakout over pre-market highs and set tight risk levels due to high volatility.
2. Short the Hype After the Spike
How It Works:
While some reverse splits create a temporary bounce, many reverse split stocks eventually sell off due to weak fundamentals.
Why It Works:
-
The reverse split can’t fix the company’s underlying issues.
-
Retail traders often jump in blindly on the bounce, driving up prices unsustainably.
-
Once the initial hype fades, the stock tends to fade back down.
How to Trade It:
-
Let the initial bounce play out (this could take hours or a few days).
-
Watch for lower highs, failed breakouts, or increased selling pressure.
-
Enter a short position with defined risk above the recent high and target key support levels.
3. Options Plays (When Available)
Not all reverse split stocks have options, but when they do, they can be highly profitable tools.
Strategy Ideas:
-
Buy puts if you expect the post-split hype to fade.
-
Call spreads can limit your risk if you’re playing a speculative upside move.
-
Straddles or strangles are useful in high-volatility setups where you expect a big move in either direction.
Caution: Liquidity may be thin on newly reverse-split stocks. Be mindful of wide bid/ask spreads.
4. Trading the Float Trap
A reverse stock split shrinks the float—often dramatically. This creates the potential for low-float momentum runners, especially in small-cap stocks.
Why It Works:
-
Less supply + any news catalyst = potential squeeze
-
Retail traders and algorithms pile in quickly
-
A tightly held float can create massive price spikes
How to Trade It:
-
Identify reverse split stocks with low float (<5M shares).
-
Scan for pre-market spikes or volume surges on news.
-
Play the momentum but keep risk tight—these stocks can turn on a dime.
5. Fundamental Fade Over Time
If the stock fails to hold gains after the reverse split, there’s often a gradual bleed-out over days or weeks.
Ideal for:
-
Swing traders who want to short a failing stock post-split
-
Traders who missed the initial move but want to catch the long-term trend
Key Signals:
-
Low volume after initial hype
-
Failed breakouts and bearish chart setups
-
Dilution news or offerings shortly after the split
The Psychology Behind Reverse Stock Splits: What Most Traders Miss
While reverse stock splits are often viewed as technical adjustments, the psychological impact they have on market participants is where much of the opportunity lies. Understanding how different types of traders interpret these events can give you an edge.
1. Institutional Perception Shift
Many institutional funds and algorithmic trading models have thresholds for the shares of stocks they’ll even consider—including minimum share prices for one share. A stock trading below $5 (often called a penny stock) is automatically excluded from many of these systems. A reverse stock split can suddenly lift the stock above that threshold, putting it back on the radar of institutions and algorithmic filters.
Even if the fundamentals haven't changed, the perception has—and that alone can drive temporary inflows of capital or automated buying. Smart retail traders can front-run this behavior by identifying when a reverse split might push a stock back into that “acceptable” range.
2. Retail Trader Misconceptions
A lot of retail traders mistakenly believe a reverse split means a company is turning things around. They see a jump in the stock price—from $0.50 to $5, for example—and assume something fundamentally positive has occurred. This leads to uninformed buying pressure, often creating brief price surges right after the split.
That’s your window as a trader or shareholder if you understand that the move is psychological and technical—not fundamental, you can fade the rally or ride it short-term with a clear plan and exit.
3. Low-Float Euphoria
Post-split, the reduced float can create low-float euphoria in the day trading world. Scanners pick up the float reduction, and chat rooms light up. Momentum builds—not because of value, but because of potential squeeze mechanics. It’s artificial, but the money is real if you time it right.
4. Fear of Dilution
On the flip side, experienced traders often anticipate that reverse splits are precursors to secondary offerings or dilution, especially in struggling small caps. After the hype cools, this fear can drag the stock down over days or weeks.
If you recognize this behavior pattern, you can structure longer-term short trades or put options as price may inevitably decline.
Bottom line: Reverse stock splits mess with perception. And markets move on perception. If you can anticipate the emotional reaction—greed, hope, fear—you can position yourself ahead of the herd and profit accordingly.
Red Flags to Watch For
Not every reverse split is tradable. Avoid getting trapped by these common pitfalls:
❌ Reverse Split with No Volume
If nobody’s trading it, there’s no edge.
❌ Overly Diluted Companies
Reverse splits are often followed by dilutive offerings, which crush the stock price.
❌ Unpredictable Price Action
Some reverse split stocks become too volatile or illiquid, making clean setups hard to execute.
❌ Illiquid Options
If you're playing through options, make sure there's enough volume and tight spreads.
How to Find Reverse Stock Splits
You can scan for upcoming or recent reverse splits using:
-
Stock screeners with reverse split filters (e.g., Benzinga Pro, Finviz Elite)
-
Press releases and company filings on SEC.gov
-
Trading communities and news aggregators that flag these setups in real time
Key Things to Keep in Mind
-
Reverse stock splits don’t create value, but they create opportunity.
-
The best profits often come from trading the reaction, not the event itself.
-
Liquidity, float, and volume are more important than the split ratio.
-
Risk management is key—these trades can move quickly in both directions.
Final Thoughts: Reverse Splits Are a Trader’s Playground
So, how to profit from a reverse stock split? You treat it like any other trade setup: identify the pattern, assess the risk, and execute with discipline. Whether you’re scalping a bounce, shorting a fade, or playing the volatility through options, reverse splits offer some of the most dynamic opportunities in the market—if you know what you’re doing.
Don’t chase blindly. Don’t fall for the hype. Use the strategies above to trade smarter, not harder.